Ques 1: Consider an enterprise network with two Ethernet segments, a web server and a firewall, connected via three routers as shown below.
GATE 2022 Q no 22
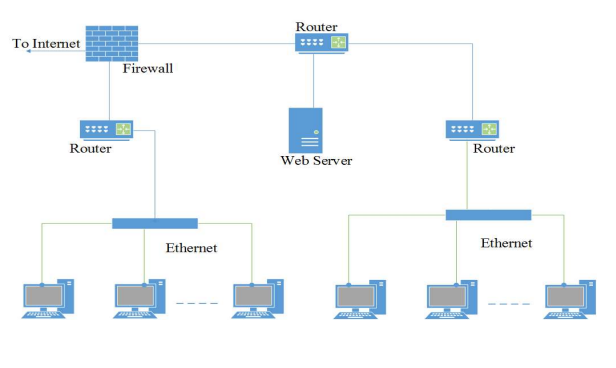
What is the number of subnets inside the enterprise network?
(A) 3
(B) 12
(C) 6
(D) 8
Ans: (C) 6
Solution: For each interface, router has one entry in routing table.
Each interface out of a router = 1 subnet
So, here 2 + 3 + 2 = 7
but 1 is common (router to router) so 7 – 1 = 6
Ques 2: Consider the resolution of the domain name www.gate.org.in by a DNS resolver. Assume that no resource records are cached anywhere across the DNS servers and that iterative query mechanism is used in the resolution. The number
of DNS query-response pairs involved in completely resolving the domain name is_____________.
GATE 2022 Q no 35
Ans: 4
Solution: Number of query-response pairs = 4.
The name of the url is www.gate.org.in and not www.gate.in.
If it was www.gate.in , then there would have been 3 pairs because of 3 levels, namely,
- root DNS server
- TLD server for .in and
- Authoritative server.
But given URL is www.gate.org.in and so there will be 4 pairs because of 4 levels, namely,
- root DNS server
- TLD server for .in
- TLD server for .org and
- the authoritative server.
Ques 3: Consider routing table of an organization’s router shown below:
GATE 2022 Q no 55
| Subnet Number | Subnet Mask | Next Hop |
| 12.20.164.0 | 255.255.252.0 | R1 |
| 12.20.170.0 | 255.255.254.0 | R2 |
| 12.20.168.0 | 255.255.254.0 | Interface 0 |
| 12.20.166.0 | 255.255.254.0 | Interface 1 |
| Default | R3 |
Which of the following prefixes in CIDR notation can be collectively used to correctly aggregate all of the subnets in the routing table?
(A) 12.20.164.0/20
(B) 12.20.164.0/22
(C) 12.20.164.0/21
(D) 12.20.168.0/22
Ans: (B) , (D)
Ques 4: Consider a network with three routers P, Q, R shown in the figure below. All the links have cost of unity.
GATE 2022 Q no 57
The routers exchange distance vector routing information and have converged on the routing tables, after which the link Q−R fails. Assume that P and Q send out routing updates at random times, each at the same average rate. The probability of a routing loop formation (rounded off to one decimal place) between P and Q, leading to count-to-infinity problem, is___________.
Ans: 0.5
Solution: Once Q-R fails then Q will immediately update its distance to R to ∞. But P will still be having some finite value (which is 2).
Now it depends on P and Q, who is sending distance vector first.
if Q sends then system becomes stable immediately but if P sends first then it will be count to infinity. Please understand that count to infinity is not some wrong thing, it is just it takes some time to stable.
Since it is given in question that both have same average rate hence probability is also 1/2 that P sends first than Q.