Python
- General Purpose
- High Level Computer Programming Language
- Developed by Python Software Foundation
- At National Research Institute for Mathematics and Computer Science located at Netherlands
- By Guido Van Rossum in 1980’s
- Versions- Python 1.0, Python 2.0, Python 3.0
- 2 major versions: Python 2 and Python 3
- Can be installed from from http://python.org/.
Features of Python:
- Interpreted: Executes code line by line
- Platform Independent : Can be run on different Operating Systems like Linux, Windows, Macintosh, Solaris etc
- Free and Open Source: Source code available and free of cost
- Rich Library Support : very vast library set
- Robust: Exceptional handling and Memory management features
- Scripts: Fewer lines of codes known as Scripts.
- Case Sensitive: It is a case-sensitive language and treats uppercase and lowercase letters differently.
- Multiple Programming Paradigms: It follows functional, structural and OOPs paradigms.
- Dynamic Typing: It checks type safety checks at run time.
- Reference Counts: It automatically deallocates objects which are nor used for a long time.
- Late Binding: Methods are looked up by name during run time.
Interactive mode is where you type commands and they are immediately executed. Example:
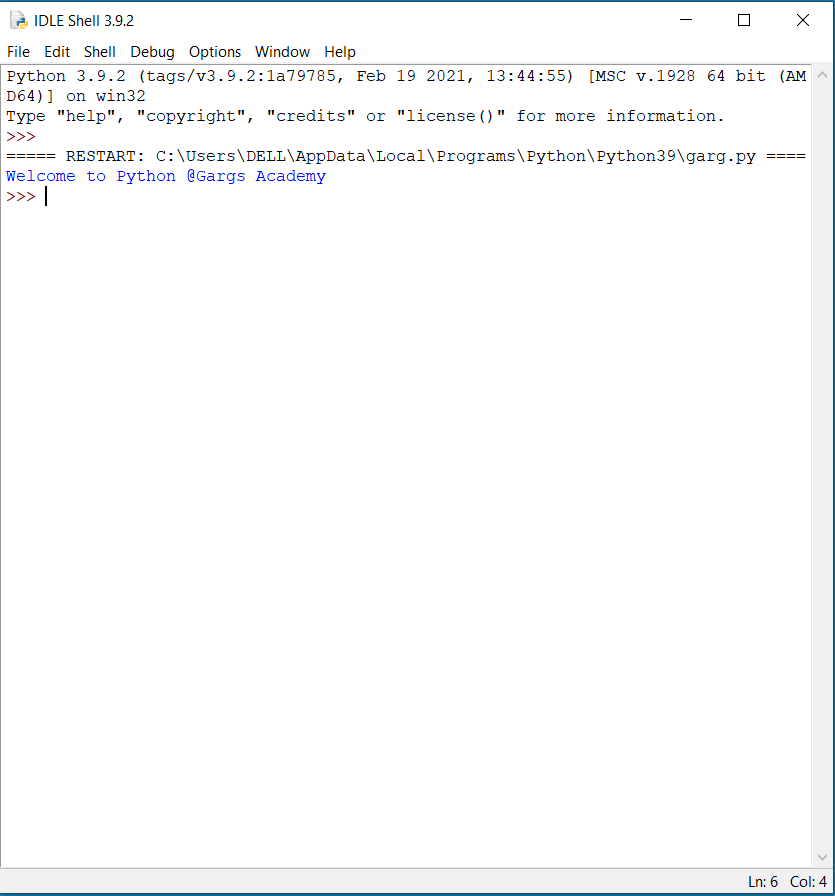
>>> print("Welecome to Python @Gargs Academy")
Welecome to Python @Gargs Academy
Script mode is where you put a group of commands into a file (a script), save it with any name (.py extension) and then Run Program to run the file.
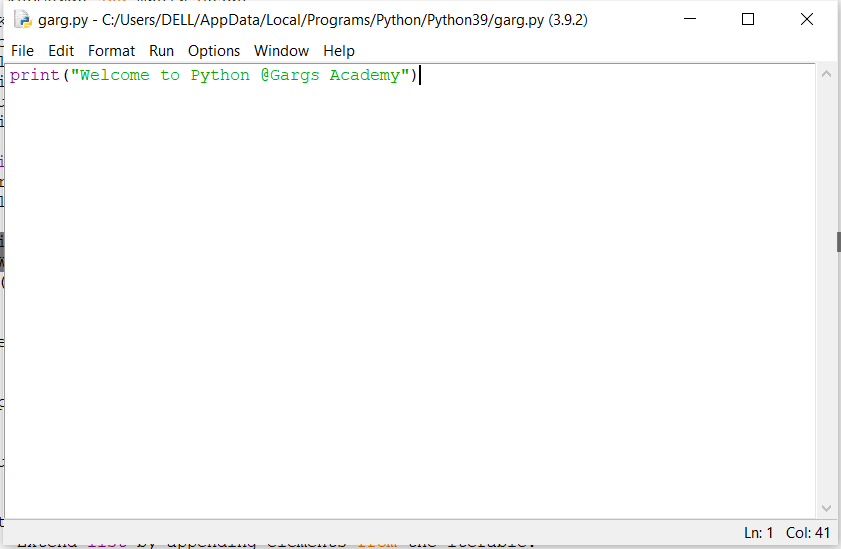
Click on Run->Run Module and output will be shown as:
Learning English:
Alphabets -> Words -> Sentences -> Paragraphs -> Essays/Stories
Learning python:
Character Set-> Tokens -> Statements -> Programs -> Projects/Softwares
Python Character Set: Python character set is the set of valid characters recognized by the Python language. Python supports all ASCII / Unicode characters:
- Alphabets: Capital (A-Z) and small (a-z) alphabets.
- Digits: 0-9.
- Special Symbols: ! ” # $ % & \ ‘ ( ) * + , – . / : ; < = > ? @ [ \ ] ^ _ ` { | } ~
- White Spaces: tab space (\t) , blank space, newline (\n) , carriage return (\r).
- Other: All ASCII and UNICODE characters are supported by Python that constitutes the Python character set.
How to check/Verify Character Set of Python
>>> import string
>>> string.printable
'0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~ \t\n\r\x0b\x0c'
>>> string.ascii_letters
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
>>> string.ascii_uppercase
'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
>>> string.ascii_lowercase
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
>>> string.digits
'0123456789'
>>> string.hexdigits
'0123456789abcdefABCDEF'
>>> string.octdigits
'01234567'
>>> string.punctuation
'!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
>>> string.whitespace
' \t\n\r\x0b\x0c'
Tokens: A token is the smallest individual unit in a python program. There are 5 types of tokens in Python:
- keywords
- Identifier
- Literal/Constant
- Operator
- Punctuator/Separator